题目
分析
这是一道离散化的经典例题,但也可以用扫描线解决。离散化已经讲过,而扫描线的介绍参见此处。
离散化、排序、去重
每个建筑可以用这样一个结构表示:
struct Building
{
int l, h, r; //左边界,高度,右边界
};
... ...
while (cin >> l >> h >> r)
{
buildings.push_back({l, h, r});
}
// 离散化:收集所有关键坐标
vector<int> coords;
for (const auto& building : buildings)
{
coords.push_back(building.left);
coords.push_back(building.right);
}
sort(coords.begin(), coords.end());
coords.erase(unique(coords.begin(), coords.end()), coords.end());假定有三个建筑: (1,5,4), (2,5,6), (3,8,7)。
显然,坐标排序去重后形成的数组为:
[1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 7]一共有六个关键点,也就是说在这6个点上高度有变化,但我们没有记录是出现建筑还是建筑结束,也没有记录建筑的高度——这个记录将在下面处理。
找到各区间的最高高度
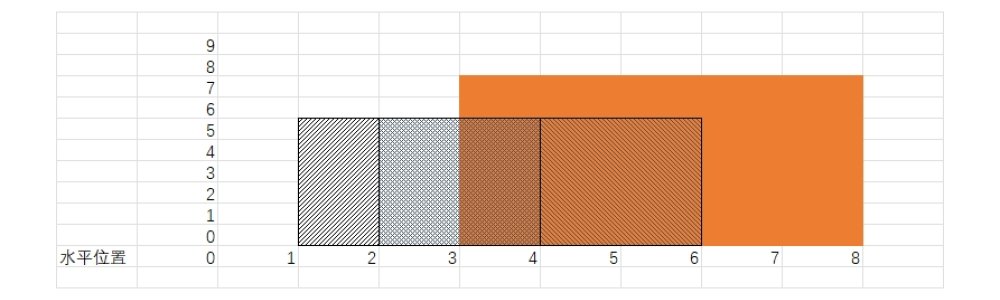
这三个建筑构成如下的形状:
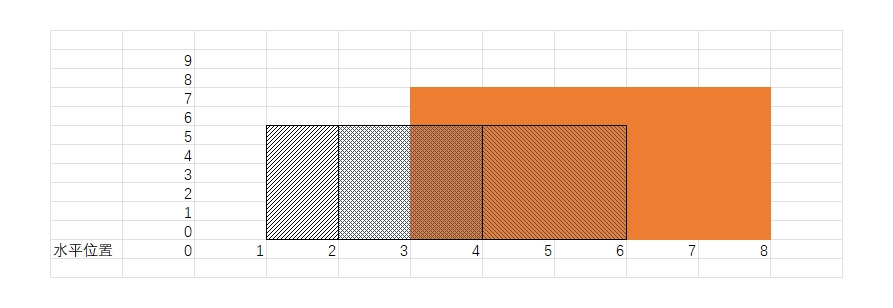
我们已经整理出6个关键点,它们形成了5个区间。建筑高度只可能在这5个区间中出现。对于每个建筑,它自己的左右边界在这个关键点中肯定会出现,但因为经过了排序,所以位置不定,需要用lower_bound去找出来。同时,在遍历这个区间时,要去看别的建筑(遍历)高度:这个区间的高度只能是最高的那个。
int n = coords.size(); //有n个独立坐标
vector<int> maxHeight(n-1, 0); //只能形成n-1个区间
for (const auto& building : buildings)
{
int leftIdx = lower_bound(coords.begin(), coords.end(), building.left) -
coords.begin();
int rightIdx =
lower_bound(coords.begin(), coords.end(), building.right) -
coords.begin();
for (int i = leftIdx; i < rightIdx; i++)
{
maxHeight[i] = max(maxHeight[i], building.height);
}
}在上面的代码中,我们遍历所有的building。对于每个building,用lower_bound在coords找到该building影响的范围([leftIdx, rightIdx))——一定能精确找到——并将这个区间的高度通过打擂台的方式更新为最高。如果没有区间永远没有哪个building覆盖,那就是缺省的0。
形成轮廓线
得到所有建筑在各自区间对高度的贡献,并最终只保留最高的高度后,我们得到了最终的maxHeight数组。注意:这里离散化的好处就体现出来了,因为我们没有记录一个区间各点的高度,只记录了关键点(也就是高度转折,也就是天际线折点)的高度。
我们遍历maxHeight数组,跟踪当前高度currentHeight(初始化为0),只要高度变化就按照题目要求加入转折点coords[i]和高度maxHeight[i],并更新当前高度。最后输出即可。
但还要注意一个陷阱:
注意到,我们在构造区间最高高度的时候,是设定[leftIdx, rightIdx),也就是说,右边界没有被设置,因为根据我们的定义,右边界的高度一定是下一个折点的高度。而最后一个建筑没有后续建筑,且它的结束点一定也是一个折点,于是我们要再补充设置最后一个坐标coords[n-1]对应了高度0。
vector<int> result;
int currentHeight = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) //注意,我们只有0-(n-2),一共n-1个区间!
{
if (maxHeight[i] != currentHeight)
{
result.push_back(coords[i]);
result.push_back(maxHeight[i]);
currentHeight = maxHeight[i];
}
}
// 最后回到地面高度0
if (currentHeight != 0)
{
result.push_back(coords[n - 1]);
result.push_back(0);
}答案
思考
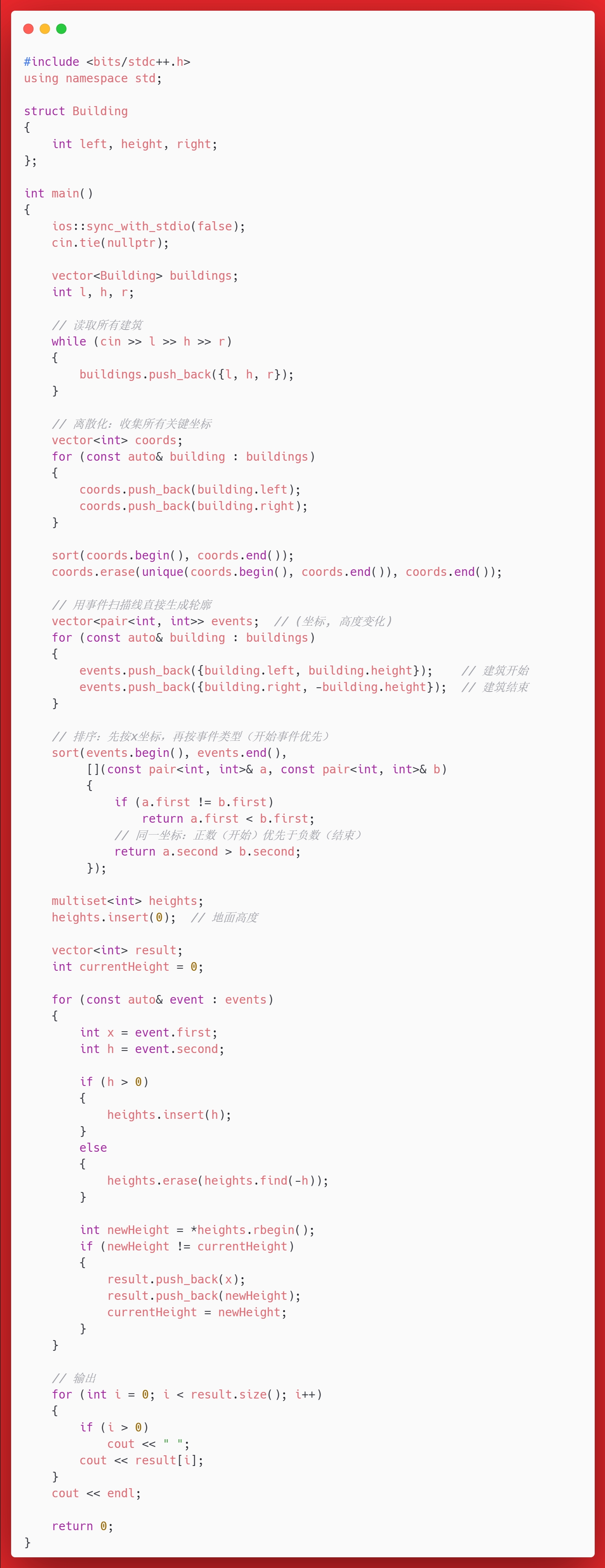
这个算法因为要遍历所有的建筑,并遍历每个建筑的左右区间,所以时间复杂度是\(O(N^2)\)。用扫描线算法可以降低时间复杂度,核心代码如下:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct Building {
int left, height, right;
};
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
vector<Building> buildings;
int l, h, r;
// 读取所有建筑
while (cin >> l >> h >> r) {
buildings.push_back({l, h, r});
}
// 用事件扫描线直接生成轮廓
vector<pair<int, int>> events; // (坐标, 高度变化)
for (const auto& building : buildings) {
events.push_back({building.left, building.height}); // 建筑开始
events.push_back({building.right, -building.height}); // 建筑结束
}
// 排序:先按x坐标,再按事件类型(开始事件优先)
sort(events.begin(), events.end(),
[](const pair<int, int>& a, const pair<int, int>& b) {
if (a.first != b.first) return a.first < b.first;
return a.second > b.second; // 正数(开始)优先于负数(结束)
});
multiset<int> heights;
heights.insert(0); // 地面高度
vector<int> result;
int currentHeight = 0;
for (const auto& event : events) {
int x = event.first;
int h = event.second;
if (h > 0) {
heights.insert(h);
} else {
heights.erase(heights.find(-h));
}
int newHeight = *heights.rbegin();
if (newHeight != currentHeight) {
result.push_back(x);
result.push_back(newHeight);
currentHeight = newHeight;
}
}
// 输出
for (int i = 0; i < result.size(); i++) {
if (i > 0) cout << " ";
cout << result[i];
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}这里用到了STL中的multiset,因为对于各个关键坐标点,有可能存在相同的高度,而取最高高度的时候不用打擂台,因为multiset会排序高度,将最高的放在最后,用*heights.rbegin()就可以得到。时间复杂度也降低为\(O(n log n)\)。